Cephalohematoma Vs Caput Succedaneum Vs Subgaleal Hemorrhage Radiology

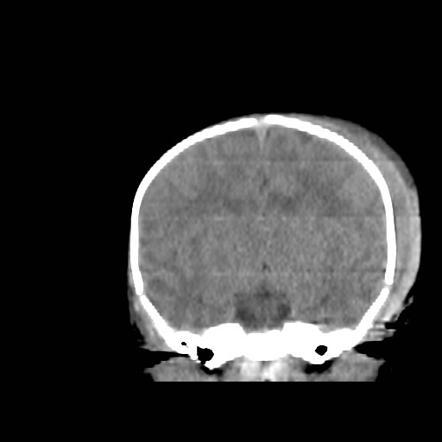
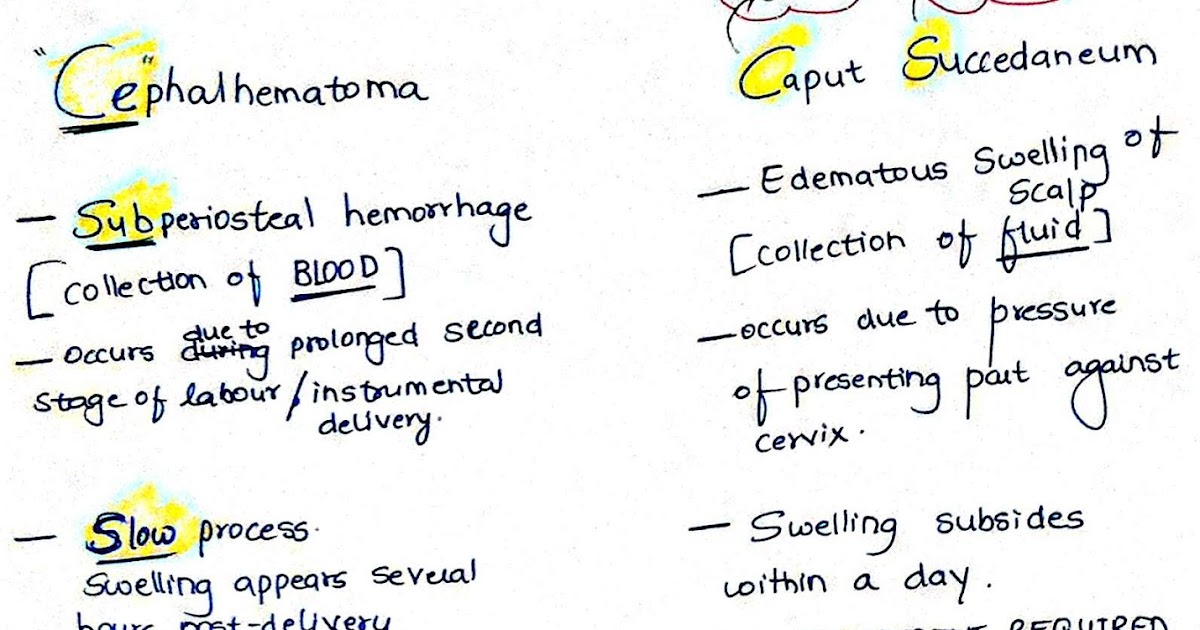
The hemorrhage is subperiosteal in cephalhematoma as opposed to the edema and blood in caput succedaneum and subgaleal hemorrhage which are located over the periosteum in either the subcutaneous or subaponeurotic spaces see fig.
Cephalohematoma vs caput succedaneum vs subgaleal hemorrhage radiology. If enough blood accumulates a visible fluid wave. Caput succedaneum results from pressure on the presenting part of the skull against the dilating cervix. Below is a table of differences between caput and cephalhematoma. Cephalohematoma vs caput succedaneum.
Chignon artificial caput succedaneum. Typically the edema is just about the size of the large egg but it can also spread in wide areas of the head. A caput succedaneum is an edema of the presenting part of the head of the baby. It often appears over the vertex of the newborn s head as a result of pressure against the mother s cervix during labor.
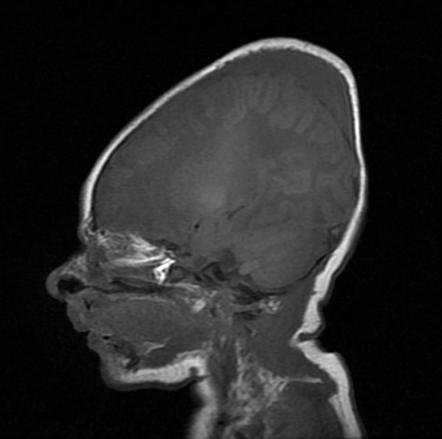
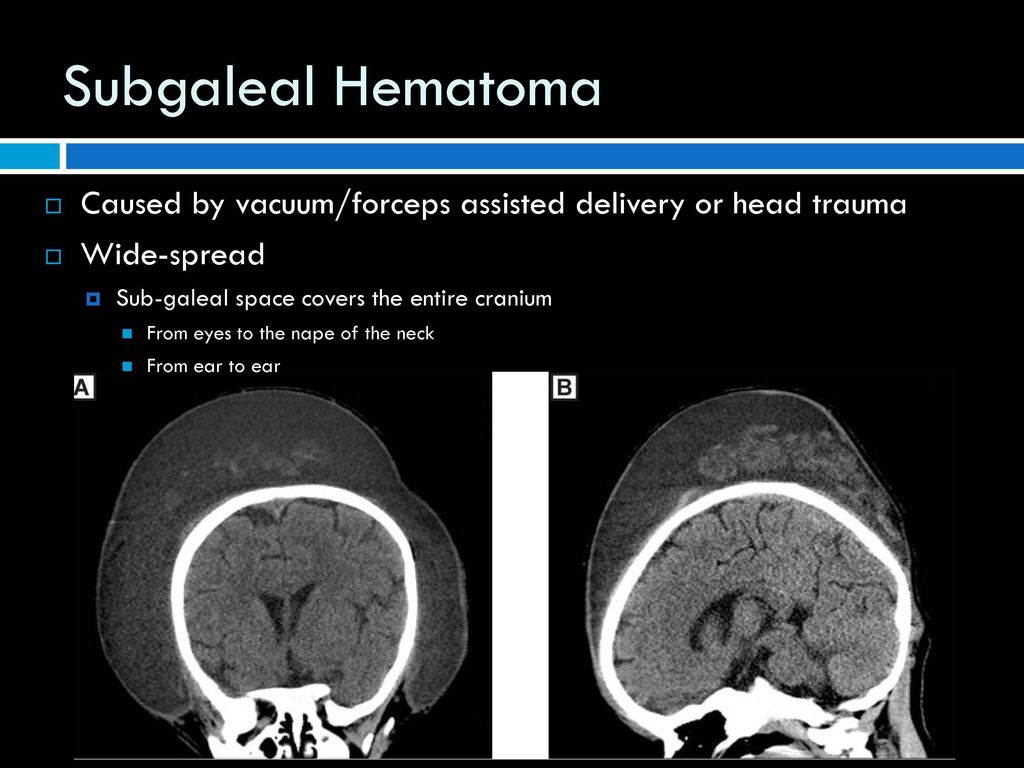
It may extend to the orbits and the subcutaneous muscles of the neck. Subgaleal haemorrhage is collection of blood beneath the galeal epicranial aponeurosis and above the periosteum. Resolves over a few days. When does it develop.
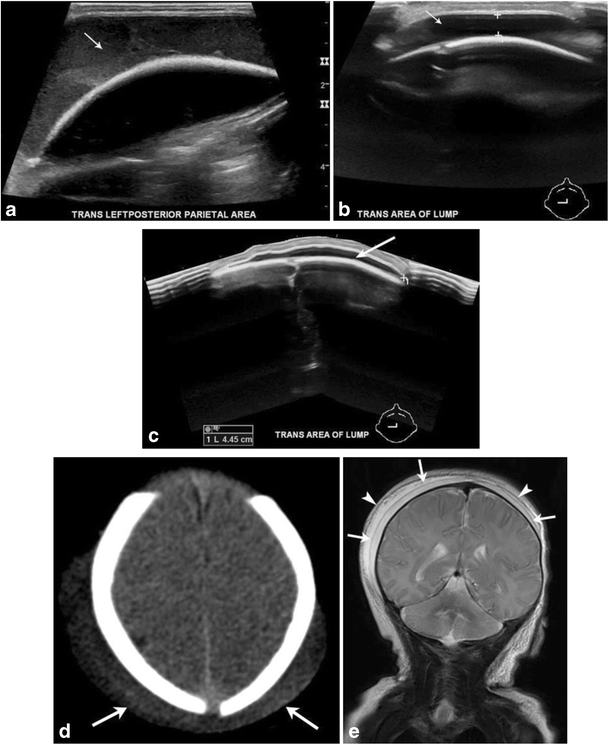
Being bound by a suture line distinguishes them from subgaleal hematoma which can cross sutures. Cephalhematoma is a collection of blood. Differential diagnosis involves distinguishing caput suc cedaneum from cephalohematoma 1 subgaleal hemorrhage should also be part of the differential diagnosis. Not limited by suture.
Subgaleal haemorrhage sgh detection and management in the newborn page 3 of 6 neonatal guideline usually at the presenting part of the scalp. Subcutaneous hemorrhage requiring no intervention. Caput succedaneum is an edema of the scalp. They are bound between the periosteum and cranium and therefore cannot cross sutures.
Subgaleal hemorrhage may initially be mistaken for caput succedaneum because blood crosses cranial suture lines in both conditions but subgaleal hemorrhage in contrast to cephalohematoma. It typically resolves within 12 18 hours and there are no complications beyond a circular area of bruising. Caput succedaneum cephalohematomas are often confused with caput succedaneum because they have the similar characteristic of swelling of the scalp. Cephalohematomas are traumatic subperiosteal hematomas of the skull that are usually caused by birth injury.
Into the subaponeurotic space from rupture of the emissary veins. Occurs after vaginal delivery. It may be imaged with ultrasound ct or mri. When does it disappear.
A collection of interstitial fluid and. The swelling is soft and puppy in nature. The difference is that caput succedaneum is a natural result of the head moving through the birth canal. Covers a much larger area than a cephalohematoma.